specirficity of orthopedic testing to rule out rotator cuff tears|torn rotator cuff test results : distributing Among tests for infraspinatus tears, external rotation lag signs at 0° had a specificity of 98% (95% CI=96% to 100%) and a likelihood ratio of 6.06 (95% CI=1.30 to 28.33), and the Hornblower’s . 17 horas atrás · Waterloo to host Times Higher Education Digital Health 2025 By Jordan Flemming. The University of Waterloo will take up the banner as host of next year's .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Tabela de classificação Superliga 2023/2024 em Livesport.com. Esta página é sobre classificação Superliga 2023/2024, (Futebol/Dinamarca). Se você está procurando por .
Finally, the “painful arc sign” has high sensitivity (97.5 percent) as a single finding, making it helpful in ruling out rotator cuff tears when absent. 2 The test is performed by having.Among tests for infraspinatus tears, external rotation lag signs at 0° had a specificity of 98% (95% CI=96% to 100%) and a likelihood ratio of 6.06 (95% CI=1.30 to 28.33), and the Hornblower’s .
Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings from the . Rotator cuff special tests. A doctor or physiotherapist can use one of more than 25 functional tests during a physical exam to diagnosis a . The physical examination maneuvers that best identify the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear are the internal rotation lag test, the external rotation lag test, and a positive.
A positive lag sign with external rotation is the best test for full-thickness tears of the infraspinatus and supraspinatus (positive likelihood ratio = 7.2). A positive lag sign with.There are a number of classification systems that are used to describe the size, location and shape of rotator cuff tears. Most commonly tears are described as partial- or full-thickness. A commonly cited classification system for full- . strength is assessed using Jobe’s Test (see below) – pain with this test is indicative of a subacromial bursitis/irritation – not necessarily a tear. Only considered positive for tear with a true drop arm. i.e. arm is brought to 90° and literally falls down.
Surgical repair has shown moderate to excellent clinical results in most studies. However, surgical treatment for chronic and large rotator cuff tears needs to be improved, especially for those in elderly patients, who continue to demonstrate .Rotator cuff tears are more common in the dominant arm — the arm you prefer to use for most tasks. If you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, there is a greater likelihood of a rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder — even if you .Rotator cuff tears are more common in the dominant arm — the arm you prefer to use for most tasks. If you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, there is a greater likelihood of a rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder — even if you have no pain in that shoulder. Several factors contribute to degenerative, or chronic, rotator cuff tears.
Rotator cuff tears are the most common upper extremity condition seen by primary care and orthopaedic surgeons, with a spectrum ranging from tendinopathy to full-thickness tears with arthritic change.
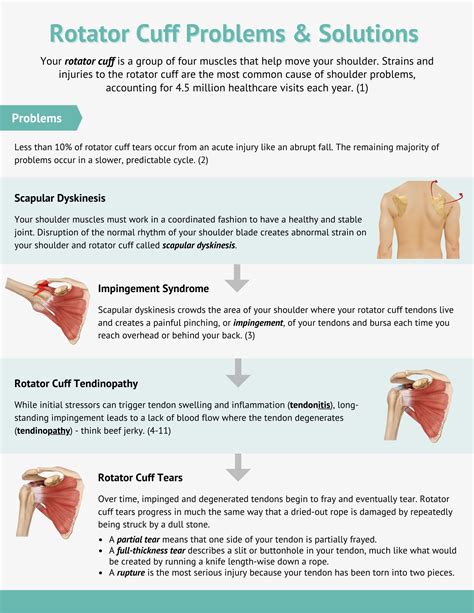
torn rotator cuff test results
Detection of rotator cuff tears: the value of MRI following ultrasound. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:450–457. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1561-9. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 19. Crowling P, Gamble A, Rangan A. The use of shoulder ultrasound in a one-stop clinic: diagnostic accuracy for rotator cuff tear and biceps tendon pathology.Rotator Cuff Tests. Supraspinatus Test (+ LR 3.2) . Refered pain & non-orthopedic causes: Referred pain from Neck; Diaphragm (e.g . Diagnosis should rely on clinical findings; cannot use imaging to rule-out tear; May give some diagnostic information: Narrowing of acromiohumeral space (<7mm) is most specific sign; May see humeral head .The rotator cuff is a common cause of pain in the shoulder. Pain can happen because of: Tendinitis — inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons. Bursitis — inflammation of the bursa. Impingement — this happens because the space between the top of your shoulder (acromion) and the rotator cuff tendons becomes smaller when you raise your arm. How To Test For A Rotator Cuff Injury. Studies suggest that rotator cuff disorders are likely responsible for up to 65-85% of all painful shoulder presentations. (1,6,7) The following section highlights the essentials of a rotator cuff exam, including how to test for shoulder impingement, an underlying culprit for up to 95% of all chronic .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus.This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies.The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as: Epidemiology. In adults, rotator cuff injury is the most common tendon injury seen and treated. Statistically, approximately 30% of adults age over 60 have a tear, and 62% of adults over 80 have tears. In Germany, a prospective study on 411 asymptomatic shoulders demonstrated a 23% overall prevalence of RC tears with 31% in those of age 70 and 51% in .
Specific Rotator Cuff Tests. As the rotator cuff comprises four separate muscles, each with different functions, testing can reveal which muscles are affected and to what extent. Though it may not be practical to perform each one during evaluation, it is .
This test is commonly used by orthopedic surgeons and sports medicine specialists. It can help distinguish between pain caused by a rotator cuff tear and pain caused by tendinitis. . If you have a rotator cuff tear, the pain will be relieved, but the muscle will remain weak. . Doctors often want to rule out other possible causes of a person .The rotator cuff tendons cover the head of the humerus (upper arm bone), helping you to raise and rotate your arm. This article provides answers to questions you may have if you have a torn rotator cuff, including information about causes, symptoms, and treatments. The O’Brien test can help diagnose a tear in the top or superior part of your labrum. A superior labrum tear is also called a SLAP tear, which stands for superior labrum, anterior to posterior. The O’Brien test can also rule out other problems, such as: Rotator cuff tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome. Prevalence of rotator cuff tears. Rotator cuff tear is a common disease. According to general population surveys, the prevalence of rotator cuff tear is 25 % in those older than 50 years of age and 20 % in those older than 20 years of age . The interesting thing is that only 1/3 of the tears cause pain and 2/3 are without pain.
The post-test probabilities that the patient will exhibit rotator cuff tears are 88.8% (at minimum) for the ERLS, approximately 100% for the dropping sign, 87.7% for the hornblower's Sign, and 92.4% for the IRLS. The post-test probabilities that the patient will exhibit rotator cuff tears are 13.8% (at maximum) for the ERLS, approximately 0.0% . Rotator cuff tears, glenohumeral joint instabilities, and labral tears are associated with an increased incidence of subacromial impingement (1). The "cluster" of tests validated to rule in/rule out subacromial impingement only indicates the . A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers the arm to . Background It is unknown which combination of patient information and clinical tests might be optimal for the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears. This study aimed to determine the diagnostic value of nine individual clinical tests for evaluating rotator cuff tear and to develop a prediction model for diagnosing rotator cuff tear. Methods This prospective cohort study .
Synopsis “Special tests” for rotator cuff–related shoulder pain (RCRSP) have passed their sell-by date. In this Viewpoint, we outline fundamental flaws in the validity of these tests and their proposed ability to accurately identify a pathoanatomical source of pain. The potential harm of these special tests comes in conjunction with imaging findings that are .This rotator cuff injury test is a common shoulder injury test and is effective and easy to carry out. Lift off Test; Also known as the Gerber Test, is one of many shoulder tests carried out to determine rotator cuff injury. The patient is asked to place the back of the hand on the small of the back and they should then lift the hand back and .
Rotator cuff tears are more common in the dominant arm — the arm you prefer to use for most tasks. If you have a degenerative tear in one shoulder, there is a greater likelihood of a rotator cuff tear in the opposite shoulder — even if you have no pain in that shoulder. Several factors contribute to degenerative, or chronic, rotator cuff tears. Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but . This movement is one of the most specific findings of biceps tendon injury. 1. Many provocative tests (i.e., Yergason, . it is difficult to rule out concomitant rotator cuff lesions. Rotator cuff tears may cause pain and limit your ability to do daily tasks. Or, a rotator cuff tear may cause no pain for some time. If you suspect you have a rotator cuff tear, reach out to your healthcare provider for advice. Most of the time, non-invasive measures can help restore shoulder function and reduce pain.
Less than half of patients with full rotator cuff tears report pain, and some may walk around with a torn rotator cuff for 20 years or longer without issues. Then, one day, they wake up with disruptive pain, day and night. In fact, sleep loss is a major reason patients seek care for rotator cuff injuries.
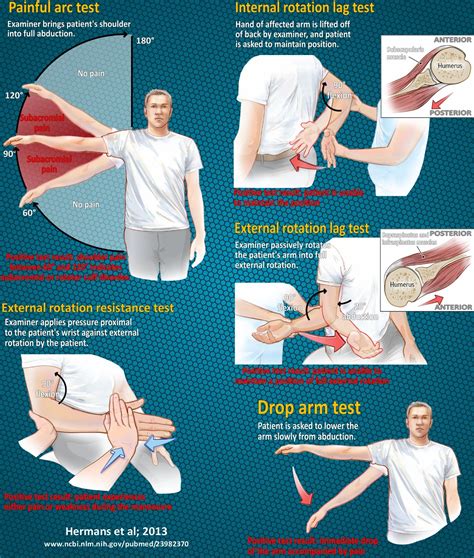
rotator cuff tests pdf
Gerar 2ª via do boleto; Teste de Velocidade; Guia MAXX; Guia de Programação; Canais
specirficity of orthopedic testing to rule out rotator cuff tears|torn rotator cuff test results